Keywords: Lab Industry's Expansion into Global Markets; International Exchanges; Made in China; Artificial Intelligence; Smart Labs; Independent Innovation; Low-carbon Development
Globally, the demand for scientific instruments remains robust, particularly in fields such as biochemistry, life sciences, biotechnology, and diagnostics, driving growth in laboratory sectors. Many enterprises within this industry are actively pursuing opportunities in international and Southeast Asian markets, fostering deeper global innovation partnerships and facilitating technology exchanges. Moreover, they are striving to establish internationally recognized brands, enhance product value, and contribute to the sustainable advancement of the economy. This year's “Two Sessions” have unveiled promising avenues for the scientific instrument industry:

1. The advent of intelligent technology heralds the onset of a new era
The future will witness a surge in demand for high-precision and high-efficiency scientific instruments, driven by the high-end, intelligent, and environmentally sustainable transformation of traditional industries, alongside the rapid expansion of emerging sectors such as new materials and renewable energy.
2.Accelerated international technology exchanges bolster independent innovation
By fostering collaborations and knowledge-sharing on a global scale, we can bolster our capacity for independent innovation, surmounting technical barriers in China's instrumentation industry. By prioritizing major scientific and technological initiatives and advancing research in game-changing and leading-edge technologies, reinforcing international cooperation and exchanges, we can provide a solid foundation for innovation within biochemical analysis and laboratory domains.
3. Prioritizing green and low-carbon initiatives is imperative for China's sustainable development trajectory.
The escalating threat posed by new pollutants and plastic pollution underscores the critical importance of energy conservation, emissions reduction, and environmental protection. These efforts will present fresh opportunities for growth within the instrumentation industry.

April 9-12, 2024, analytica, the world's leading trade fair for laboratory technology, analysis and biotechnology, will kick off at the prestigious Trade Fair Center Messe München in Germany. analytica 2024 promises an array of enriching experiences including booth displays, the analytica Conference, supporting forums, and a host of related activities. This year's event will spotlight the cutting-edge concept of the Smart Lab 4.0, offering insights into intelligent analytical instruments, innovative smart laboratory technologies, and network solutions designed for the laboratories of tomorrow.
- Lab 4.0: more efficiency and flexibility in the lab of the future
- Robots and cobots: laboratory automation for digital transformation
- Connectivity: standard interfaces for laboratory networking
- Virtual Reality: how to expand the laboratory world
Lab 4.0: more efficiency and flexibility in the lab of the future
Efficient workflows are essential for the competitiveness of any laboratory, as this is the only way to cope with the increasing demands imposed by various factors, including new legal regulations Automated laboratory processes and optimized workflows reduce the workload of laboratory personnel. The software and hardware in Lab 4.0 is also designed to be modular and flexible enough to respond quickly to users' individual requirements and to varying sample volumes.
Processes that can be controlled via the smartphone facilitate daily work in Lab 4.0, as does the cloud-based management of all lab data.
As the quality of analysis results remains paramount, digital tools already play a key role in the collection, evaluation and storage of measurement results. Artificial intelligence is becoming more and more important in managing data glut.
Virtual Reality: how to expand the laboratory world
Individually designing and optimizing laboratory environments, simulating and improving analysis processes, practicing and assimilating individual steps: Virtual reality technologies are expanding the realm of routine laboratory analysis and diagnostics. Plus, they visualize research results. As well as viewing their microscopic images on the screen, soon cell biologists will be able to take a virtual stroll around the interior of their objects of study. And that's just one example.
Augmented reality glasses also offer helpful features for the digital lab. They can give lab staff instructions on workflows and automatically record the steps performed at the same time. Moreover, smartglasses can detect errors in the workflow and display warnings. Sample information and safety instructions when working with critical chemicals can also appear automatically in the viewer's field of view.
Robots and cobots: laboratory automation for digital transformation
Lab 4.0 is highly automated. The advantages are obvious: automated processes compensate for the shortage of skilled workers and allow high sample volumes to be handled quickly. At the same time, automation makes the laboratory safer, by reducing the risk of injury and contamination.
Automated processes and laboratory robots really come into their own when dealing with hazardous substances, pathogenic germs and harmful chemicals, but even in trace analysis, manual sample contact should be kept to a minimum to avoid contamination. Automation is also a real boon for work steps that require extreme precision.
While routine processes such as pipetting can be completely automated, other laboratory processes use cobots that work hand in hand with humans. Automation and networking solutions are also indispensable for the desired 24/7 operation.
Connectivity: standard interfaces for laboratory networking
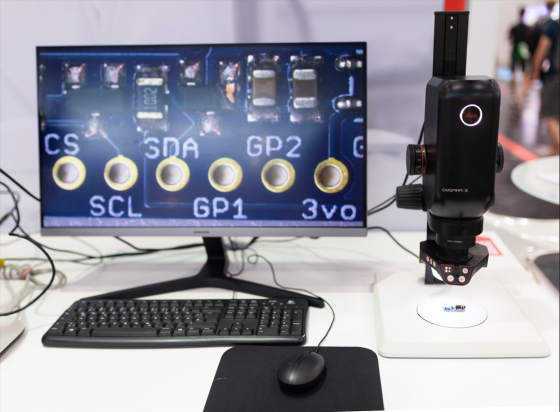

In the intelligent laboratory of the future, analytical and laboratory devices, sensors, processes and data are networked with each other and with all players in the laboratory world. These networks are controlled by laboratory information management systems (LIMS) and, increasingly, by cloud-based solutions.
It is crucial that all laboratory data is kept in a single location, with IT security measures in place, and is easily accessible to other systems, laboratory personnel and external users, such as customers or authorities.
Comprehensive integration in Lab 4.0 relies on standardized interfaces. All devices must have compatible network access and drivers so they can communicate with each other, their users and the cloud. Systematic digital transformation of the laboratory is not confined to analytical equipment and laboratory technology, but incorporates all data streams, workflows, software and hardware as well as people with their expertise and knowledge. The usual mix of devices made in different years by various manufacturers presents laboratories with a particular challenge.
The OPC UA (Open Platform Communications Unified Architecture) standard established for industrial automation forms a good basis for laboratory networking. analytica brings you up to date on the Laboratory Agnostic Device Standard, or LADS for short, which complements OPC UA.

analytica China is a spin-off exhibition of analytica, the International Trade Fair for Laboratory Technology, Analysis, Biotechnology and Diagnostics, addresses one of the industry's most important growth markets in Asia, i.e. China. Since its first edition in Shanghai, China in 2002, analytica China has become the biggest trade fair in China even in Asia. The exhibition is held every two years where the latest technologies and products will be displayed. Meanwhile, the current technical conferences are the focuses of industry players as well.
Contact us:
Vivi Feng
Tel:021-20205685
Email:vivi.feng@mm-sh.com